Table of Contents
Definition of Research methodology:
Research methodology refers to the systematic process of collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data in a research study. It outlines the procedures and techniques that researchers follow to investigate a particular topic or problem and to draw valid conclusions. Research methodology is crucial because it ensures that the research findings are reliable, valid, and reproducible.
A research methodology describes the techniques and procedures used to identify and analyze information regarding a specific research topic. It is a process by which researchers design their study so that they can achieve their objectives using the selected research instruments. It includes all the important aspects of research, including research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and the overall framework within which the research is conducted. While these points can help you understand what is research methodology, you also need to know why it is important to pick the right methodology.
Key Components Of Research Methodology
- Research Design: This involves outlining the overall strategy and structure of the research, including the type of study (e.g., qualitative, quantitative, mixed-methods), data collection methods, and analysis techniques.
- Data Collection: This step involves gathering relevant data or information to address the research questions or objectives. Data collection methods can vary depending on the research design and may include surveys, interviews, experiments, observations, or analysis of existing data.
- Data Analysis: Once the data is collected, it needs to be analyzed to identify patterns, trends, or relationships. Data analysis techniques can vary widely depending on the nature of the data and the research objectives. Common techniques include statistical analysis, qualitative coding, and thematic analysis.
- Interpretation: After analyzing the data, researchers interpret the findings in the context of existing literature, theories, or frameworks. This step involves drawing conclusions, making connections between findings, and discussing implications for theory, practice, or policy.
- Validity and Reliability: Ensuring the validity and reliability of research findings is crucial in research methodology. Validity refers to the accuracy and truthfulness of the research findings, while reliability refers to the consistency and repeatability of the results.
- Ethical Considerations: Researchers must adhere to ethical principles and guidelines throughout the research process, including obtaining informed consent from participants, protecting their confidentiality, and ensuring that the research does not cause harm.
- Documentation and Reporting: Finally, researchers document their methodology and findings in a research report or paper, following the conventions of their discipline and providing sufficient detail for others to evaluate and replicate the study if necessary.
Overall, research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting rigorous and credible research, guiding researchers through each stage of the research process from planning to reporting. It helps ensure that research is conducted in a systematic and transparent manner, thereby enhancing the credibility and reliability of the findings.
Why is research methodology important?
Research methodology is crucial for several reasons:

- Guiding the Research Process: Methodology provides a structured framework for conducting research. It outlines the steps, procedures, and techniques to be used in collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data.
- Ensuring Validity and Reliability: A well-defined methodology helps ensure that the research findings are valid and reliable. Validity refers to the accuracy and truthfulness of the research results, while reliability refers to the consistency and repeatability of the findings. By following rigorous methodologies, researchers can enhance the validity and reliability of their studies.
- Minimizing Bias: Research methodologies help minimize bias by providing guidelines for sampling, data collection, and analysis. By adhering to systematic approaches, researchers can reduce the influence of personal biases and ensure that their findings are objective and impartial.
- Optimizing Resource Utilization: Effective methodologies help researchers optimize the use of resources such as time, money, and manpower. By clearly defining research objectives, selecting appropriate methods, and establishing efficient procedures, researchers can maximize the productivity and efficiency of their studies.
- Facilitating Replication: A well-documented methodology enables other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings. Replication is essential for validating research results and building confidence in the reliability of scientific knowledge.
- Ethical Considerations: Research methodologies often include ethical guidelines for conducting studies involving human participants or sensitive data. By adhering to ethical principles, researchers can ensure that their studies are conducted responsibly and with respect for the rights and welfare of participants.
Overall, research methodology is essential for ensuring the quality, credibility, and integrity of research studies across various disciplines. It provides a systematic framework for conducting research, minimizing bias, optimizing resource utilization, and upholding ethical standards, ultimately contributing to the advancement of knowledge and understanding in the respective fields of study.
Types of research methodology
There are various types of research methodologies, each suited to different research objectives, questions, and contexts. Some common types of research methodologies include:

- Quantitative Research: This type of research focuses on collecting numerical data and analyzing it using statistical methods. Quantitative research aims to quantify relationships, patterns, and trends, and it often involves structured data collection methods such as surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis of existing datasets.
- Qualitative Research: Qualitative research aims to explore and understand phenomena in-depth, often focusing on the meanings, perspectives, and experiences of participants. Qualitative methods include techniques such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and content analysis. This approach generates non-numerical data and emphasizes interpretation and understanding rather than quantification.
- Mixed-Methods Research: Mixed-methods research integrates both quantitative and qualitative approaches within a single study. Researchers use mixed-methods to gain a comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena, combining the strengths of quantitative analysis (e.g., statistical generalization) and qualitative analysis (e.g., rich contextual insights).
- Experimental Research: Experimental research involves manipulating variables to observe their effect on outcomes. This type of research typically includes a control group and an experimental group and aims to establish cause-and-effect relationships. Experimental designs are common in fields such as psychology, medicine, and social sciences.
- Descriptive Research: Descriptive research aims to describe characteristics, behaviors, or conditions within a population or phenomenon. It involves observing and recording data without manipulating variables. Descriptive studies often use surveys, observations, or case studies to provide a detailed overview of a particular topic.
- Correlational Research: Correlational research examines the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them. It seeks to identify associations or correlations between variables, helping researchers understand the degree and direction of relationships. Correlational studies do not establish causation but can provide valuable insights into patterns and connections.
- Case Study Research: Case study research focuses on in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. It involves intensive data collection through methods such as interviews, observations, and document analysis to explore complex phenomena within a specific context. Case studies are common in fields such as business, education, and psychology.
These are just a few examples of research methodologies, and researchers often adapt or combine different approaches based on the specific research questions, objectives, and constraints of their study. Each methodology has its strengths and limitations, and the choice of methodology depends on factors such as the research topic, goals, available resources, and disciplinary conventions.
t
What are data collection methods?
Data collection methods refer to the techniques and procedures used to gather data from individuals, groups, or sources for research or analysis purposes. Different data collection methods are chosen based on the research objectives, the nature of the data, and practical considerations. Some common data collection methods include:
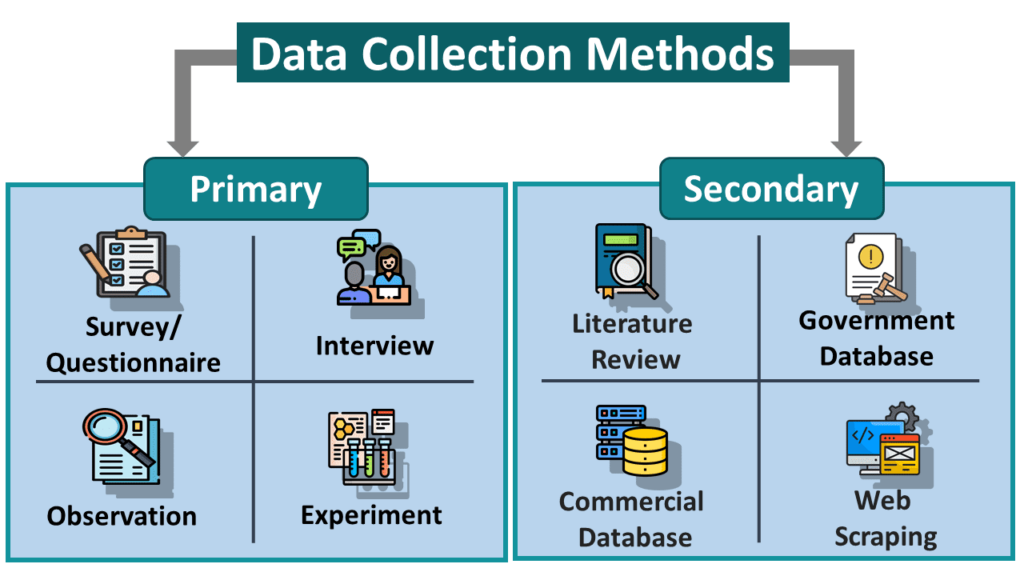
- Surveys: Surveys involve asking questions to individuals or groups to gather information about their opinions, attitudes, behaviors, or characteristics. Surveys can be administered through various means, including paper-based questionnaires, online surveys, telephone interviews, or face-to-face interviews.
- Interviews: Interviews involve direct interaction between a researcher and a participant to gather detailed information about their experiences, perspectives, or opinions. Interviews can be structured (with predetermined questions), semi-structured (with a flexible guide), or unstructured (open-ended), depending on the research goals and context.
- Observations: Observational methods involve systematically watching and recording behaviors, interactions, or phenomena in their natural settings. Observations can be participant observations (where the researcher actively participates) or non-participant observations (where the researcher remains an observer). This method is commonly used in ethnographic research and studies of human behavior.
- Experiments: Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables to observe their effect on outcomes while controlling for other factors. Experimental designs allow researchers to establish causal relationships between variables. Data collection in experiments often involves measurements, observations, or surveys administered before and after the experimental manipulation.
- Document Analysis: Document analysis involves systematically examining written, visual, or audiovisual materials such as texts, reports, newspapers, photographs, or videos to extract relevant information. This method is useful for studying historical events, organizational documents, policy analysis, and content analysis of media.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups involve bringing together a small group of individuals to discuss a specific topic guided by a moderator. Focus groups encourage interaction and discussion among participants, providing insights into shared attitudes, perceptions, or experiences. This method is commonly used in market research, product development, and social sciences.
- Secondary Data Analysis: Secondary data analysis involves using existing data collected for other purposes, such as government surveys, databases, or organizational records. Researchers analyze secondary data to address new research questions or complement primary data collection efforts. Secondary data analysis can be cost-effective and time-saving but may be limited by data availability and quality.
These are some of the commonly used data collection methods in research. Researchers often employ a combination of methods to triangulate findings, enhance validity, and capture diverse perspectives. The choice of data collection method depends on factors such as the research objectives, the nature of the research questions, the characteristics of the population or phenomena under study, and the available resources.
