Table of Contents
Definition
Creativity is a complex and multifaceted concept that has been defined in various ways depending on the context and the discipline. However, at its core, It is the ability to generate ideas, solutions, or insights that are original, novel, and valuable. It involves combining and recombining existing elements in new ways to produce something that is both new and useful.
Creativity is not limited to the arts or design fields; it is essential in all areas of human endeavor. For example, scientists use creativity to come up with new hypotheses and experiments, engineers use it to design innovative solutions to complex problems, and entrepreneurs use it to create new products and services that meet market needs.
There are many theories and models that attempt to explain how it works and what factors contribute to it. These include the four Ps of creativity (process, person, product, and press), the investment theory (which suggests that creativity is a combination of hard work, talent, and preparation), and the systems model of creativity (which views creativity as a dynamic interplay between individual, social, and environmental factors).

The Creativity Process
The creativity process can be understood as a series of stages or steps that individuals typically go through when they are engaged in a creative activity. While different models may have varying numbers of stages, there are commonly four main stages associated with creativity: preparation, incubation, illumination, and verification.
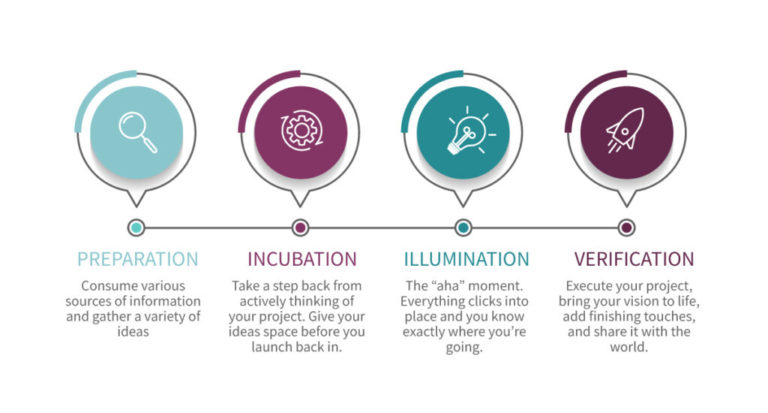
- Preparation: This stage involves gathering information, exploring the problem, and considering different perspectives. Individuals might consciously or unconsciously work on the problem, but no new ideas emerge during this phase.
- Incubation: This stage involves stepping away from the problem and allowing the unconscious mind to process information. It’s often marked by a period of rest or engaging in a different, unrelated activity. This phase is where ideas may start to develop below the surface of conscious awareness.
- Illumination: Also known as the “Aha!” moment, illumination is the sudden appearance of a solution or idea. It can come seemingly out of nowhere after a period of incubation. This phase is often marked by a feeling of clarity and excitement.
- Verification: This stage involves evaluating the idea or solution and determining its feasibility and value. It often requires refining and testing the idea to ensure it is practical and aligns with the problem or goal.
It’s important to note that these stages are not always linear and can overlap or repeat. Additionally, different creative tasks may require different approaches and may not follow a strict pattern. However, understanding the general stages of the creative process can be helpful in recognizing and supporting.
The systems view of creativity
The systems view of creativity is an approach to understanding creativity that emphasizes the complex interplay of various factors that contribute to creative outcomes. This perspective treats creativity as a multi-level, dynamic, and interactive process that involves not only the individual, but also the social and environmental contexts in which the individual operates.

The systems view suggests that creativity arises from the interaction between different elements, such as:
- The Individual: This includes personal characteristics such as cognitive abilities, personality traits, domain-specific knowledge, and skills. It also includes cognitive processes, such as memory, attention, perception, and problem-solving.
- The Social Environment: This refers to the social and cultural context in which the individual operates. It includes social norms, cultural values, social networks, and group dynamics. Social interactions and collaborations can influence it by providing diverse perspectives, feedback, and resources.
- The Physical Environment: This refers to the physical context in which takes place, such as the physical workspace, resources, tools, and technologies available. A conducive physical environment can support creativity by providing resources, reducing distractions, and promoting experimentation.
- The Domain or Field: This refers to the specific domain or field in which the creative work is taking place, such as science, art, business, or technology. Each domain has its own conventions, rules, and standards, which can both constrain and enable creativity.
The systems view of creativity highlights the importance of considering the interactions between these different elements and recognizing that creativity is not solely a property of the individual, but rather emerges from the dynamic interplay between the individual and their environment. This perspective encourages researchers and practitioners to consider a holistic approach to creativity that takes into account the various factors that contribute to creative outcomes.
How To Be A Creative
Becoming more creative involves engaging in certain practices and developing specific mindsets that can help you think more imaginatively, generate original ideas, and solve problems in new and innovative ways. Here are some strategies that can help foster creativity:
- Open-mindedness: Be receptive to new ideas, perspectives, and experiences. Approach problems with curiosity and a willingness to explore unconventional solutions.
- Risk-taking: Don’t be afraid to take risks and make mistakes. Creativity often requires experimenting with new approaches and being open to failure as a part of the learning process.
- Playfulness: Adopt a playful attitude toward problem-solving. Engage in activities that stimulate your imagination and encourage creative thinking, such as brainstorming, doodling, or playing with objects.
- Persistence: Creative breakthroughs often require persistence and effort. Don’t give up if an idea doesn’t work immediately; instead, keep exploring and iterating until you find a solution that works.
- Collaboration: Work with others to bounce ideas off of each other and gain different perspectives. Collaboration can provide valuable feedback and spark new ideas.
- Mindfulness: Practice mindfulness techniques, such as meditation, to improve focus and reduce distractions. Being present and focused can help you engage more deeply with the creative process.
- Continuous learning: Stay curious and actively seek out new knowledge and skills. Learning from diverse fields can help you make unexpected connections and generate new ideas.
- Flexibility: Be willing to adapt and change your approach as needed. Flexibility allows you to adjust to new information or unexpected challenges and find creative solutions.
- Reflection: Take time to reflect on your creative process and outcomes. What worked well? What could be improved? Reflecting on your experiences can help you learn and grow as a creative thinker.
- Positive mindset: Cultivate a positive attitude toward your creative abilities and potential. Believe in your capacity to generate unique and valuable ideas.

Remember that creativity is a skill that can be developed and nurtured over time. By practicing these strategies and embracing a creative mindset, you can enhance your ability to think creatively and approach challenges with fresh perspectives.
Why Creativity is Crucial for Success?
It is crucial for success because it enables individuals and organizations to:
- Problem-solving: Creative thinking allows for the generation of new and innovative solutions to complex problems, enhancing an organization’s ability to adapt to changing circumstances and seize opportunities.
- Differentiation: It helps individuals and organizations stand out in a crowded marketplace by offering unique products, services, or approaches.
- Innovation: it is the cornerstone of innovation, driving the development of new products, services, processes, and business models that can drive growth and profitability.
- Competitive advantage: A culture of creativity fosters continuous improvement and keeps an organization ahead of its competitors.
- Adaptability: Creativity enables individuals and organizations to adapt to change, which is a key component of success in today’s fast-paced and dynamic business environment.
- Engagement: Creativity fosters employee engagement, as it allows individuals to express their ideas, contribute to the organization’s success, and feel a sense of ownership over their work.
- Leadership: Creative leaders are more likely to inspire and motivate their teams, leading to higher levels of productivity and performance.
- Customer Satisfaction: Creativity helps organizations meet customer needs in innovative and unexpected ways, leading to higher levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Resilience: Creativity allows individuals and organizations to find new opportunities in the face of challenges and setbacks, making them more resilient in the long run.
- Sustainability: Creative thinking can lead to the development of sustainable business practices that balance profitability with environmental and social responsibility.

In summary, creativity is crucial for success because it drives innovation, differentiation, problem-solving, adaptability, and resilience. It fosters engagement, leadership, and customer satisfaction, and promotes sustainable business practices. By fostering a culture of creativity, individuals and organizations can set themselves up for long-term success in a rapidly changing world
